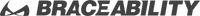Osgood Schlatter Disease in Adults: Tips, Exercises & Treatment
What is Osgood Schlatter Disease?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a condition characterized by a painful inflammation (bony knob or spur) located under your kneecap (patella).
The cause of Osgood Schlatters is irritation on your growth plate (tibial tuberosity), where your patellar tendon attaches to your shinbone (tibia).
What does that mean?
During a growth spurt, children and adolescents’ thigh muscles (quadriceps) don’t always keep up with the growth of their thighbone (femur). As their quadricep muscle stretches, it pulls on their patellar tendon, which connects their kneecap to their shinbone. This repeated tension and irritation causes pain, swelling, inflammation, and sometimes the formation of a bump under kids’ knees.
Do Adults Get Osgood Schlatter Disease?
The good news is that Osgood-Schlatter disease, commonly referred to as the growing pains of your knees, usually goes away after you’ve stopped growing, usually between 14 and 18 years old. Therefore, this disease is rare among adults but not unheard of! Luckily, adults with Osgood-Schlatter disease normally only have one affected knee and don’t experience too much pain.
Don’t worry if you have Osgood-Schlatter disease as an adult, although it is rare, you are not alone! Anybody who had Osgood-Schlatters as a child is more likely to keep getting it as an adult. In fact, about 10% of patients with Osgood-Schlatters continue to experience some symptoms into adulthood. Similar to kids, adults can also get this disease if they participate in repetitive physical activities and sports, including basketball, volleyball, figure skating, etc.
What Causes Osgood Schlatter Disease in Grown-Ups?
Unfortunately, some people continue to have pain from Osgood-Schlatter disease even after they are fully grown. This is usually caused by bone fragments left from when your bone was replacing cartilage in your knee. These fragments can be left in your patellar tendon from unresolved Osgood-Schlatters and irritate your knee. Most adults experience similar Osgood-Schlatters symptoms in comparison to kids and adolescents with the disease.
Top 4 Treatment Options for Adults with Osgood Schlatters
Do you have Osgood-Schlatter disease as an adult? If so, check out the different treatment methods below, which help both children and adults!
-
Resting and Icing Your Knee
Resting the knee, elevating it, and icing can all help drain any excess swelling and inflammation, which can help alleviate the pain. If you experience pain during a physical activity, you should take a break from that activity.
Follow the R.I.C.E. treatment plan to eliminate irritation and manage pain associated with Osgood-Schlatter disease. Rest is probably the most important thing you can do to treat Osgood-Schlatter disease.
If necessary, cut back on weight-bearing activities and put a cold compress on your knee to help bring the inflammation down. Do this about 3 times each day for 10 to 15 minutes each time. A bag of frozen vegetables or BraceAbility’s cold compression knee brace works great.

-
Osgood Schlatter Disease Surgery
In extreme cases, surgery may be used to get rid of Osgood-Schlatter disease in adults with recurrent symptoms. The primary purpose of surgery is to remove the bone fragments that are causing irritation on your tendon. By removing the bone fragments, you should be able to function fully without pain from Osgood-Schlatter disease.
-
Osgood Schlatter Disease Brace
A knee brace is extremely helpful if you are unable to refrain from pain-producing activities and could benefit from some extra stability. Thankfully, BraceAbility has a number of knee supports to help manage Osgood-Schlatter disease, including braces, straps, and knee sleeves for adults and children. Wearing a brace can help you get back to playing soccer, basketball, running, skating, or climbing stairs without pain.

-
Osgood Schlatters Exercises & Stretches
Stretching your muscles before and after you participate in sports or other physically exerting activities is another important element of Osgood Schlatter's treatment for adults and children.
Physical therapy exercises help strengthen your quadriceps and hamstring muscles, which can help reduce tension where your patella tendon attaches to your shin. This can also help stabilize your knee joint.
Make sure to stretch the following muscle groups:
- Quadriceps
- Hamstrings
- Iliotibial band
For specific exercises and stretches, check out this video:
Osgood Schlatter Disease Vs. Patellar Tendonitis
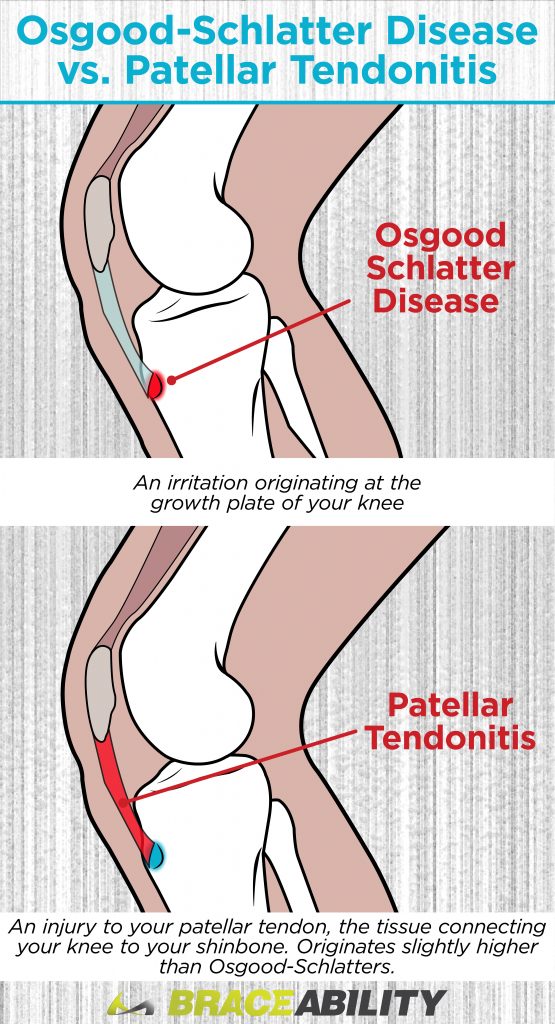 Sometimes Osgood-Schlatter disease is confused with patellar tendonitis, especially among adults. In comparison to Osgood-Schlatter disease, patellar tendinitis is an injury to your patellar tendon, the tissue connecting your knee to your shinbone.
Sometimes Osgood-Schlatter disease is confused with patellar tendonitis, especially among adults. In comparison to Osgood-Schlatter disease, patellar tendinitis is an injury to your patellar tendon, the tissue connecting your knee to your shinbone.
Pain associated with patellar tendonitis is located slightly higher than Osgood-Schlatter disease, as opposed to where your patellar tendon attaches to your shinbone.