Facet Syndrome
What Exactly Is A Facet Joint?
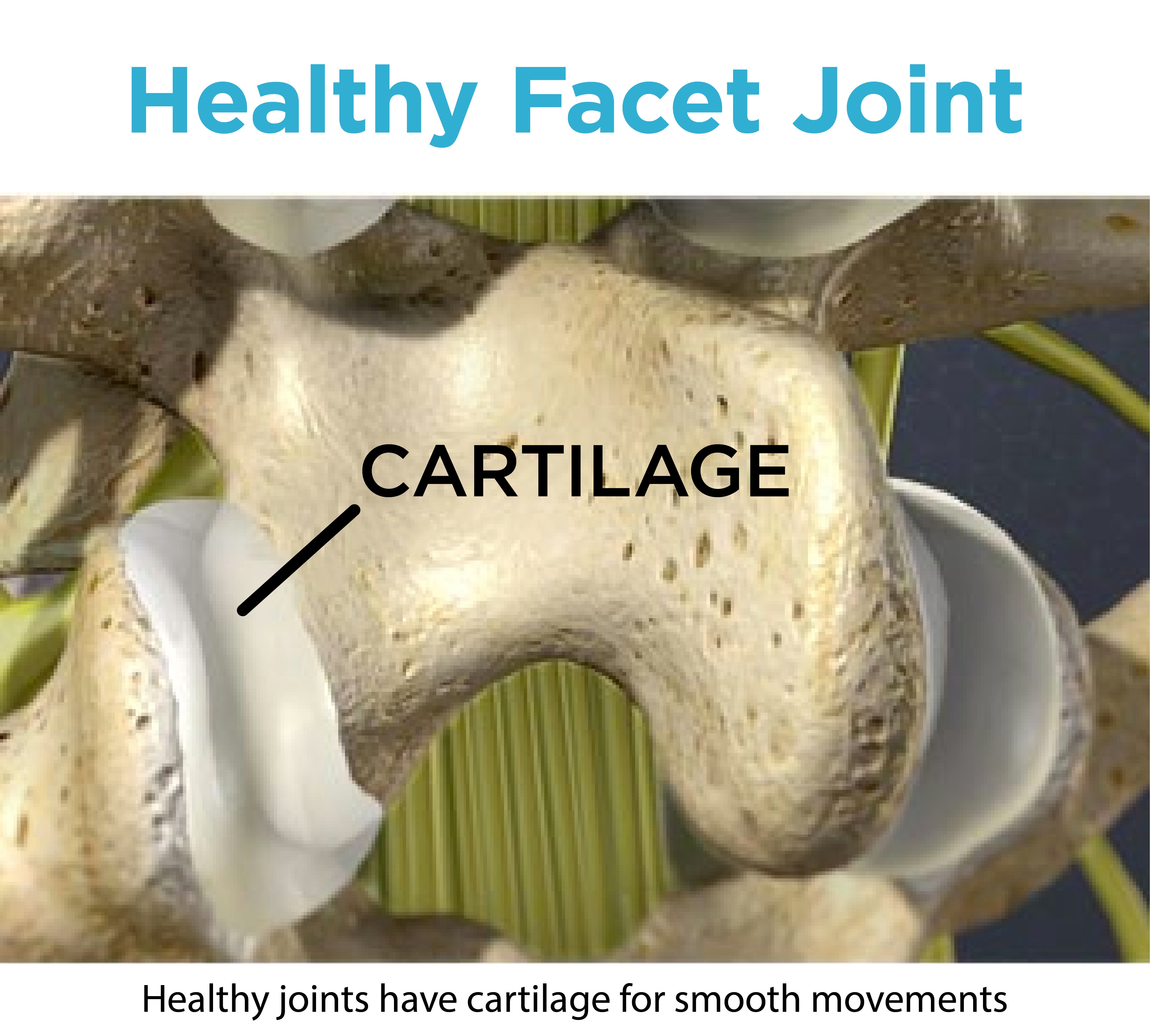 To fully understand what facet syndrome is, it’s important to know the function and role your facet joints play (also referred to as zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) in your vertebrae. To break it down, let’s start with understanding the anatomy of your spine or vertebrae.
To fully understand what facet syndrome is, it’s important to know the function and role your facet joints play (also referred to as zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) in your vertebrae. To break it down, let’s start with understanding the anatomy of your spine or vertebrae.
Your spine consists of 26 bones stacked upon each other, making up your vertebrae. Your vertebrae can be divided into three sections: lumbar (lower), thoracic (middle), and cervical (upper or neck) regions. For every bone in your spine, you have three joints accompanying it: two facet joints (one facing up and the other facing down) in the back and one large spinal disc in the front.
These facet joints are located in the back of your spine and perform a hinge-like motion connecting each vertebra. Your spinal nerves exit your spinal cord through these joints and each consists of cartilage to allow your bones to move freely without irritation. The facet joints enable your spine to complete different motions such as twisting, bending, walking, running, etc.
So What Is Facet Joint Syndrome?
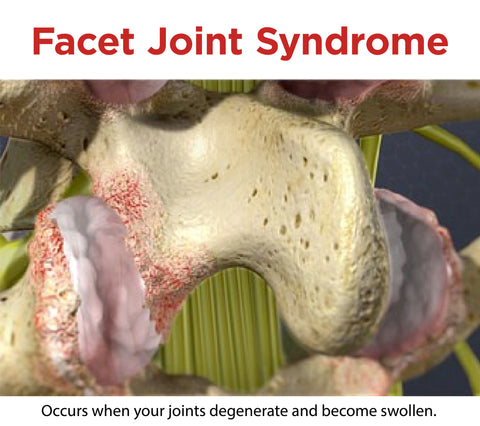
Facet syndrome, also called facet joint disease, is a common and debilitating condition in which you experience pain and tenderness in your spine. Facet joint pain occurs when your joints degenerate and become swollen, which leads to pain and discomfort. This condition can occur in any region of your spine but is more likely to be found in your lumbar or lower back region (L1 through L5 vertebrae).
What is Causing Pain from Facet Joint Syndrome?
The most common cause of facet joint pain is the natural aging process when your joints degenerate over time, reducing the amount of cartilage in between each bone. Facet joint syndrome is heavily related to and can even be interchangeable with osteoarthritis of the spine, which is when your cartilage surrounding your bone wears down, which in turn causes swelling and pain. Sound familiar?
Other risk factors for facet joint arthritis include:
- Being an obese individual: Wondering if you’re overweight? Use this calculator to find out.
- Overuse of your spine - from sports or from incorrectly lifting heavy objects (learn 7 proper lifting techniques)
- Family history of facet joint syndrome
- Other diseases that may increase your risk of developing facet syndrome include gout, other forms of arthritis, or infections
- Injuries or trauma to the spine such as a fall, whiplash, or excessive twisting in the lumbar, thoracic, or cervical region of your back
What Are Common Facet Disease Symptoms?
Do you believe you have facet syndrome? The most frequent symptom of facet disease is difficulty twisting or bending your spine. For those who have cervical facet syndrome, you might experience trouble twisting or turning your neck left or right. Whereas those who have lumbar facet syndrome may have difficulty straightening or getting up from a seated position.
Other symptoms may include:
- Pain, numbness, and muscle weakness, especially in the beginning or end of the day
- Tenderness in your lower, middle, or upper back region
- Discomfort when leaning forwards or backward
- For lumbar facet syndrome: you may experience back pain radiating down to the back of your legs or buttock areas
- For cervical facet syndrome: you may experience neck pain radiating down to your shoulders or arms
- Headaches located behind your eyes or ringing in your ears
- Abnormal Curvature of your spine
Could My Poor Posture Result in Facet Syndrome?
Poor posture has many bad side effects including chronic back pain, migraines, lower energy levels, heart problems, poor digestion, lack of oxygen flow, and even facet syndrome. Poor posture results in extra stress being placed on your joints, muscles, and vertebrae. This extra stress can be placed specifically on your facet joints, which can lead to irritation and inflammation. Your poor posture may result in the loss of cartilage in between your joints and bones.
Luckily for you, fixing your posture can be very simple! Wearing a posture brace can be your first step to perfect posture. These braces help train your muscle memory in the right position, with your shoulders back. For those who work at a sedentary job, poor posture can be difficult to avoid especially after sitting in the same spot for a majority of your day. Learn 6 simple steps to pain-free posture while sitting at your desk.
Wondering how good or bad your current posture is? Take our quiz now to find out!
Can being Obese or Overweight Cause Facet Disease?
Lower back pain and obesity are highly correlated: extra weight that you might be carrying around forces your spine to try to hold your midsection upright. This in turn makes your muscles, joints, and bones to work harder, making you more susceptible to injuries and pain.
Since facet syndrome is more common in your lumbar region, obesity may play a role in your facet disease. Losing weight can be a way to help eliminate or even treat your facet disease. Exercises and stretches to help strengthen your core are ways to lose weight while reducing the chance that your facet syndrome will progress.
Read more about other back conditions that affect plus size men and women.
Decoding The Different Names & Variations for Facet Syndrome
There are many different names or similar conditions that involve the facet joints, which can lead to quite a bit of confusion. Luckily for you, we’re here to break it down to help you understand your painful condition. The conditions below are either a variation of facet syndrome or are a related condition.
What is facet arthropathy?
Facet arthropathy is similar to facet syndrome in that it causes discomfort and pain to your spine in a similar manner. Facet arthropathy is a disease or an abnormality in your facet joints usually caused by degeneration or arthritis.
Symptoms of arthropathy are comparable to facet syndrome as it includes lower back pain, especially when twisting, sitting, or bending. It’s also common for those who have cervical facet arthropathy to experience pain or discomfort when moving your neck. The difference is that you usually don’t experience pain radiating down your legs or buttocks with lumbar facet arthropathy.
For those who have mild facet arthropathy, it’s common for you to have another condition alongside this one that might be contributing to your symptoms. Such conditions include spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, and other spinal injuries.
To help treat your pain from arthropathy, try avoiding movements that may cause further injury or cause you discomfort. In addition, you can try anti-inflammatory medications and physical therapy exercises.
If those don’t help, another facet arthropathy treatment option is an epidural steroid injection to help reduce the pain and tension. These injections help reduce inflammation and swelling that surrounds your joints. The downside to such injections is that you may have to get multiple, as these aren’t a permanent solution to this condition. As a last resort, you may have to have back surgery known as spinal fusion.
What is facet hypertrophy?
Facet hypertrophy refers to the degeneration and enlargement of the joints. The enlargement of the joints may be the response of the overuse of your spine trying to provide stability, which in turn causes your body to produce more bone tissue around your joints (called bone spurs). This extra bone tissue results in enlargement that can place pressure and tension on the nerves that travel throughout your spine.
It’s more common to have facet hypertrophy in your lumbar or lower back region and usually occurs in individuals over 30, as it relates to the overtime use of your spinal joints. Some symptoms of mild facet hypertrophy include stiffness, discomfort when moving your back, trouble walking or running, and a hunched posture position.
To treat bilateral facet hypertrophy, your doctor may advise you to take anti-inflammatory medications, exercises to help strengthen your back muscles, posture correctors, or physical therapy. If those methods are ineffective or if you have a severe case of hypertrophy, you may have to endure surgery such as spinal fusion or open spine facet joint surgery to help relieve the pressure placed on your spinal nerves.
What is facet arthrosis?
Facet arthrosis refers to the degeneration of your spine similar to facet hypertrophy (above) in which you have bone growths or bone spurs that enlarge the facet joints. These bone spurs tend to grow so that it may place tension on surrounding tissues and nerves. The most common region for bilateral facet arthrosis is typically in the lumbar region of the spine.
Symptoms include pain, tingling, or numbness in the regions that are affected. In addition, you may experience trouble moving, walking, or doing daily activities. To treat facet arthrosis, you may have to have surgery to remove the bone spurs.
What’s the Difference Between Lumbar, Thoracic, & Cervical Facet Syndrome?
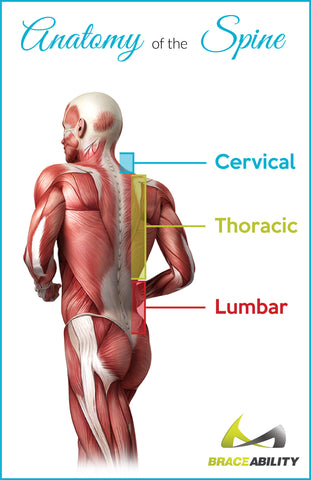
Facet joint syndrome can occur in any region of your spine, lumbar, thoracic, or cervical. But the most common form of facet syndrome occurs in your lumbar or lower back region. Pain in your lower back pain is very common as this may mean you could have a variety of conditions including degenerative disc disease, osteoarthritis, spinal stenosis, obesity-related back pain, spine curvature disorder, and more.
As mentioned previously, those who have lumbar facet syndrome experience difficulty straightening or getting up from a seated position, and back pain radiating down to the back of your legs or buttock areas. Lumbar facet disease is most common in your L4-L5 or L5-S1 region of your lumbar spine.
The second most common form of facet syndrome is cervical facet syndrome. Common symptoms of this condition include trouble twisting or turning your neck left or right, neck pain radiating down to your shoulders or arms, and headaches located behind your eyes or ringing in your ears. Cervical osteoarthritis is more common later in life, as the cause is highly related to degeneration of the joints in your cervical or neck area. There is not a specific region that is more prone to facet syndrome, leaving C1-C7 vulnerable to this condition.
The least common region for facet disease is the thoracic region of the spine because it tends to be the least flexible of the areas and is made to provide stability for your back. This inflexibility protects your spine from hyperextending or whiplash, which can be a cause of this condition. Although it protects you from one aspect, degeneration of the spine can occur in all the regions of your back. Symptoms are similar to the ones listed above and may be felt in your upper back, chest, or arms.
Facet Joint Disease Conservative Treatment Options
To start, your doctor may recommend trying conservative treatment methods to help alleviate your pain. Some options include:
- Rest: It’s advised to take a break from activities that may irritate your condition such as high contact sports.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to help strengthen your core, back, and shoulders can help take off the extra stress that may be placed on your spine that is causing you pain. These exercises can also help stretch out your nerve muscles.
- Cold and hot therapy: It’s no surprise that using ice packs can help reduce your inflammation but in addition, using hot packs can help promote blood flow around your joints. Try our heat and ice therapy lower back wrap to help your discomfort.
- Taking anti-inflammatory medications: Taking such medications can help reduce your pain for an amount of time while also reducing swelling in the area of injury. If your pain persists, your doctor may prescribe a higher dose of medications.
- Back braces: Medical supports can help immobilize your lumbar, thoracic, and cervical regions. This immobilization can help prevent you from extending your back. It’s advised not to wear such braces for a long period of time while treating facet syndrome because you don’t want your muscles or joints to stiffen or tighten up.
- Exercises: It’s important to stay away from exercises or stretches that may cause further injury or pain. Some facet joint pain exercises have been proven to help is yoga and Pilates. These facet syndrome exercises place emphasis on your core muscles and balance, which can help prevent hyperextension of your spine and provide stability.
Cervical, Thoracic, & Lumbar Facet Injections
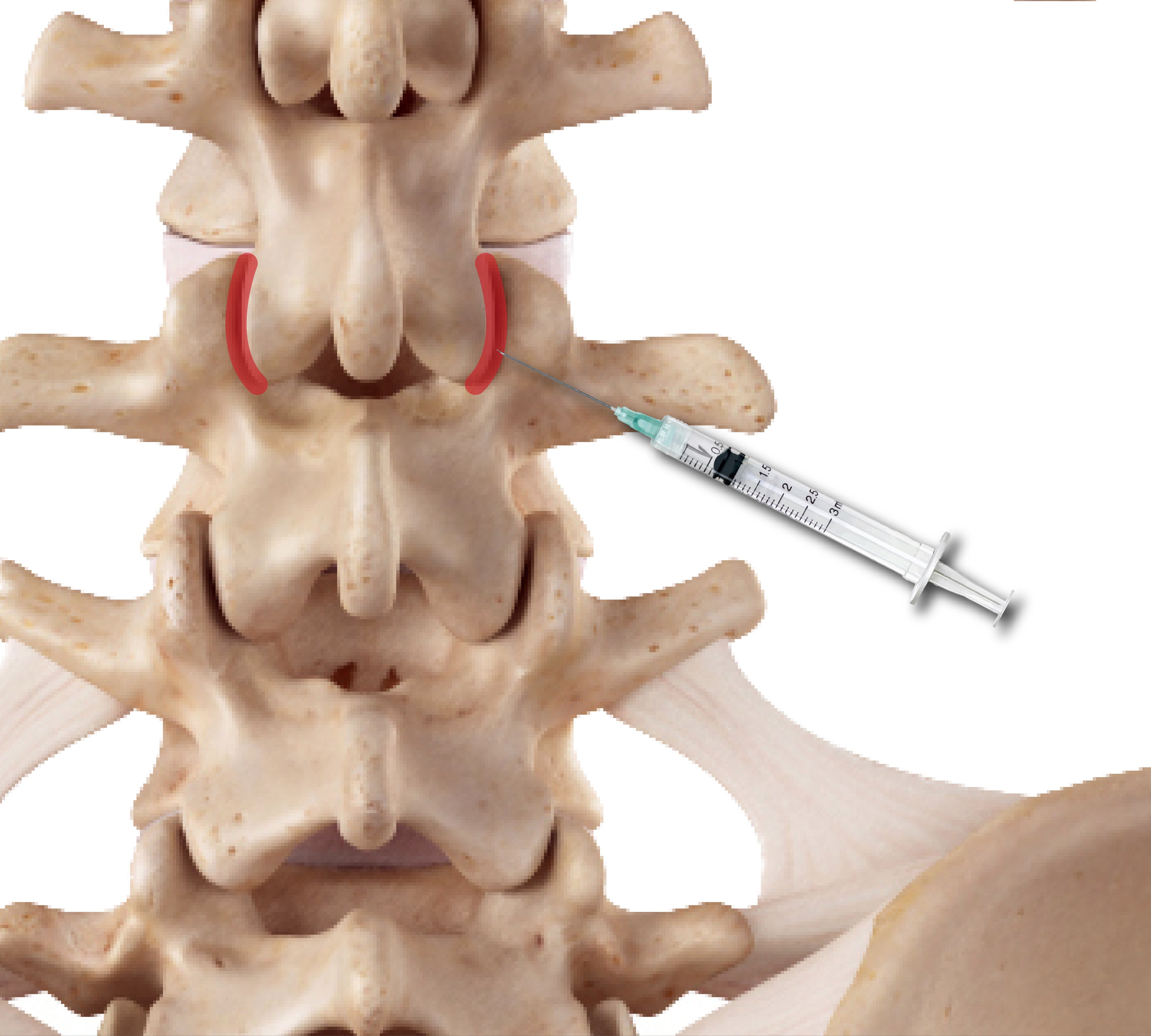
Another common treatment method for facet pain is joint blocks, otherwise known as facet injections. These facet block injections serve a dual purpose and can be very beneficial. A facet joint injection involves injecting anesthetic medication into your facet joint. These facet blocks help numb your joints to help your doctor identify the joint that is causing pain. They aim to give you pain relief while also figuring out what may be the underlying issue in your joints.
One thing to take in consideration when thinking about trying a facet injection is that just like the facet arthropathy epidural injections above, these are only a temporary solution. While this may provide relief, you may have to get multiple shots to continue numbing the irritated joint.
If while using a facet injection you don’t find any relief or you still feel pain, it’s likely you do not have an issue with the facet joint.
Do I Need Facet Joint Surgery?
If your facet syndrome worsens, surgery may be performed to help alleviate your symptoms and reduce the extra pressure that may be being placed on your nerves. There are different surgery options and ultimately is up to your surgeon in which one would be best for your specific condition. The three options are:
- Discectomy: This surgery removes part of the spinal disc that may be injured and that is causing pressure on your spinal cord.
- Laminectomy: This involves the removal of your lamina, which is a section in your vertebra, which enables more space and room for your spinal cord.
- Foraminotomy: This surgery aims to widen the spaces in between your vertebrae, which decompress nerve roots making them able to pass freely throughout your spine.