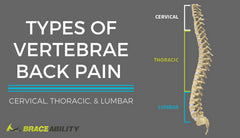
Do I Have Spinal Stenosis in My Lumbar, Cervical, or Thoracic Back Region?
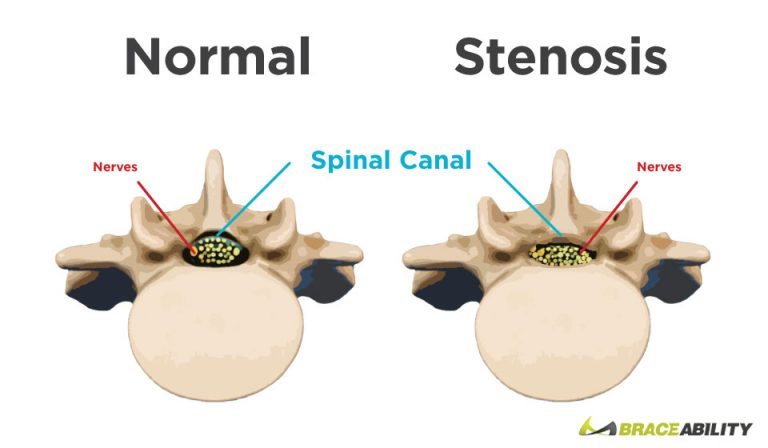 Your spine is made up of 26 bones stacked upon each other creating your vertebrae. In between each of these bones are cushioned discs, which help prevent rubbing of the bones together. Spinal stenosis is a condition that occurs when spaces in between those discs narrow, leading to extra pressure being put on your spinal cord.
Your spine is made up of 26 bones stacked upon each other creating your vertebrae. In between each of these bones are cushioned discs, which help prevent rubbing of the bones together. Spinal stenosis is a condition that occurs when spaces in between those discs narrow, leading to extra pressure being put on your spinal cord.What Are the Different Symptoms of Cervical, Thoracic, & Lumbar Spinal Stenosis?
The impact of spinal stenosis depends upon the severity of the compression as well as where in the back this occurs. There are three different regions of your spine: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar. Each of these areas has a diverse range of symptoms:
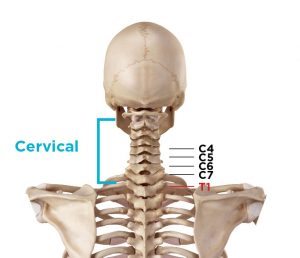 Cervical (neck) spinal stenosis symptoms: Symptoms include pain, numbness, weakness or tingling in the leg, foot, shoulder arm or hand. You may feel a burning, tingling, or numbness in your neck, shoulders, arms, or hands. Severe spinal stenosis symptoms in this area might disrupt the function of one’s bladder or bowels and it could lead to incontinence.
Cervical (neck) spinal stenosis symptoms: Symptoms include pain, numbness, weakness or tingling in the leg, foot, shoulder arm or hand. You may feel a burning, tingling, or numbness in your neck, shoulders, arms, or hands. Severe spinal stenosis symptoms in this area might disrupt the function of one’s bladder or bowels and it could lead to incontinence.
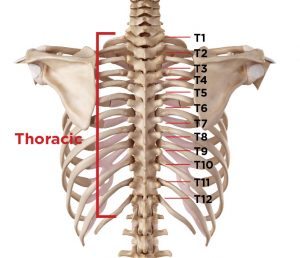 Thoracic (middle) spinal stenosis symptoms: The symptoms of stenosis in the mid-back area are a bit different from symptoms of spinal stenosis in the neck or low back because, in this region, the vertebrae are attached to the ribs. Therefore, thoracic spinal stenosis symptoms might include a limited ability to rotate the torso or move from side to side. This can also cause pain in the back or ribs and possibly radiate pain down the back or legs. Some with thoracic spinal stenosis experience aching legs and/or trouble walking. Bowel or bladder dysfunction is also possible with thoracic spinal stenosis. Since the thoracic spine is naturally narrower than other regions of the spine, spinal cord compression and the loss of sensation or movement might come on more quickly in the mid-back region. Because the answer to the question “can spinal stenosis cause paralysis?” is yes, it is important to seek medical attention quickly if you suspect the spinal cord is compromised. Luckily, this type of spinal stenosis is the least common type.
Thoracic (middle) spinal stenosis symptoms: The symptoms of stenosis in the mid-back area are a bit different from symptoms of spinal stenosis in the neck or low back because, in this region, the vertebrae are attached to the ribs. Therefore, thoracic spinal stenosis symptoms might include a limited ability to rotate the torso or move from side to side. This can also cause pain in the back or ribs and possibly radiate pain down the back or legs. Some with thoracic spinal stenosis experience aching legs and/or trouble walking. Bowel or bladder dysfunction is also possible with thoracic spinal stenosis. Since the thoracic spine is naturally narrower than other regions of the spine, spinal cord compression and the loss of sensation or movement might come on more quickly in the mid-back region. Because the answer to the question “can spinal stenosis cause paralysis?” is yes, it is important to seek medical attention quickly if you suspect the spinal cord is compromised. Luckily, this type of spinal stenosis is the least common type.
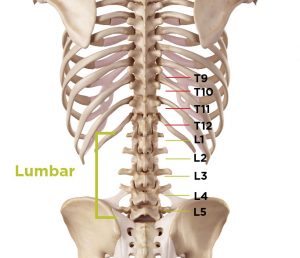 Lumbar (lower) spinal stenosis symptoms: Lumbar (lower) spinal stenosis symptoms: Lumbar spinal stenosis is the most common type of this condition. This type compresses the nerves in your lower back into your legs, which can cause a variety of symptoms. Some symptoms of this type of spinal stenosis can include mild to lower back pain, weakness in the legs or buttock area. In addition, you may have trouble balancing or notice a decrease in your coordination leading to difficulty walking, standing, or bending over. You also might experience a burning, tingling, or numbness in your back and legs. In severe cases, you might have bladder issues. Check out BraceAbility’s selection of spinal stenosis treatment products that can reduce or eliminate these unpleasant symptoms.
Lumbar (lower) spinal stenosis symptoms: Lumbar (lower) spinal stenosis symptoms: Lumbar spinal stenosis is the most common type of this condition. This type compresses the nerves in your lower back into your legs, which can cause a variety of symptoms. Some symptoms of this type of spinal stenosis can include mild to lower back pain, weakness in the legs or buttock area. In addition, you may have trouble balancing or notice a decrease in your coordination leading to difficulty walking, standing, or bending over. You also might experience a burning, tingling, or numbness in your back and legs. In severe cases, you might have bladder issues. Check out BraceAbility’s selection of spinal stenosis treatment products that can reduce or eliminate these unpleasant symptoms.
What Is Causing My Pain from Spinal Stenosis?
The most common spinal stenosis cause is simply the toll aging takes on your body. Degeneration over time can lead to the following culprits for stenosis of the neck and back symptoms:- Thickened ligaments
- Herniated or bulging discs
- Excess bone growth at the joints (bone spurs)
- Deterioration of the facet joints
- Compression fractures
How Can I Treat Cervical, Thoracic, & Lumbar Spinal Stenosis?
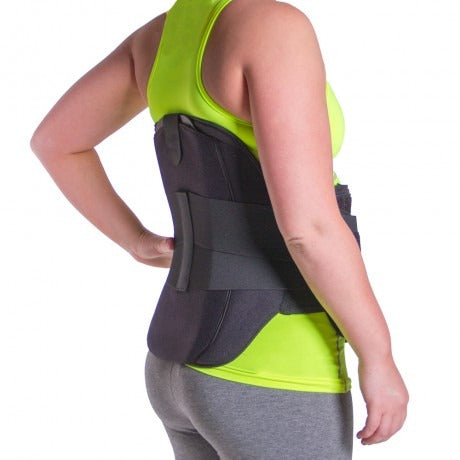 There are a number of conservative treatments you can try for relieving discomfort associated with spinal stenosis including but not limited to:
There are a number of conservative treatments you can try for relieving discomfort associated with spinal stenosis including but not limited to:- Taking anti-inflammatory medications or painkillers
- Wearing medical braces for spinal stenosis
- Exercises such as biking swimming, yoga, and stretching
- Receiving a steroid injection or nerve blocks
- Weight loss helps to remove the extra pressure that is put on the spine